
If you’re interested in the meaning of a particular term, click it on the list below to jump straight to the definition.
- Alt Text
- Anchor Text
- Backlink
- Black Hat SEO
- Broken Link
- Click Through Rate (CTR)
- Domain Authority
- Featured Snippet
- Google Penalty
- Header Tag
- Internal Link
- Keywords
- Link Building
- Local Search
- Local Search Marketing
- Long Tail Keyword
- Meta Descriptions
- Organic Traffic
- Panda
- Paid Traffic
- Penguin
- PPC
- SEM
- SEO
- SERP
- Title Tag
- White Hat SEO
- 301 Redirect
- 404 Error
Alt Text
Alt text, or image alternative text, refers to a section of HTML code that represents the text that will appear if the image fails to load. Alt text is also used to tell search engines and users with visual impairments what is shown in the image.
See code sample below. The bold section is the image alt text.
<img src=”example.png” alt=”Example Alt Text”>
Anchor Text
Anchor text refers to the text that is used when linking from one site to another. For example, if you include a sentence saying “click here for more information on our products” if you link from the words “click here” that is your anchor text. On most websites this will appear as blue text and will sometimes be underlined.
See code example below. The bold section is the anchor text.
</p><a href=”http://example.com/products”>Click here</a>for more information on our products</p>
Backlink
A backlink is a link from one website to another. So if Website A links to Website B, then Website B has a backlink.
Black Hat SEO
Black hat SEO refers to SEO practises that are against search engine guidelines. Black hat SEO techniques are designed to trick Google and other search engines into increasing the rankings of websites that don’t necessarily deserve it.
Although black hat SEO can have some quick results, if Google discovers any practises on your website that are against their guidelines (eg. buying links), your website will be penalised and essentially drop off the face of Google.
Broken Link
A broken link is a link that leads to an error page. This could be because the original page was moved or removed, or due to a mistake in the URL used to create the link.
Click Through Rate (CTR)
Click through rate (CTR) refers to the ratio of people who click on your ad in comparison to the number of people who see it.
To work out click through rate (CTR), take the number of clicks on an ad (clicks) and divide it by the number of people who saw the ad (impressions).
Clicks / Impressions = CTR
For example, if your ad had 100 views and 9 clicks, your click through rate would be 9%.
9 / 100 = 0.09 (or 9%)
Domain Authority
Domain authority (DA) is a score developed by Moz that is an approximation of how well a website will be ranked by search engines based on a number of factors including age, number of links, quality of links, and popularity.
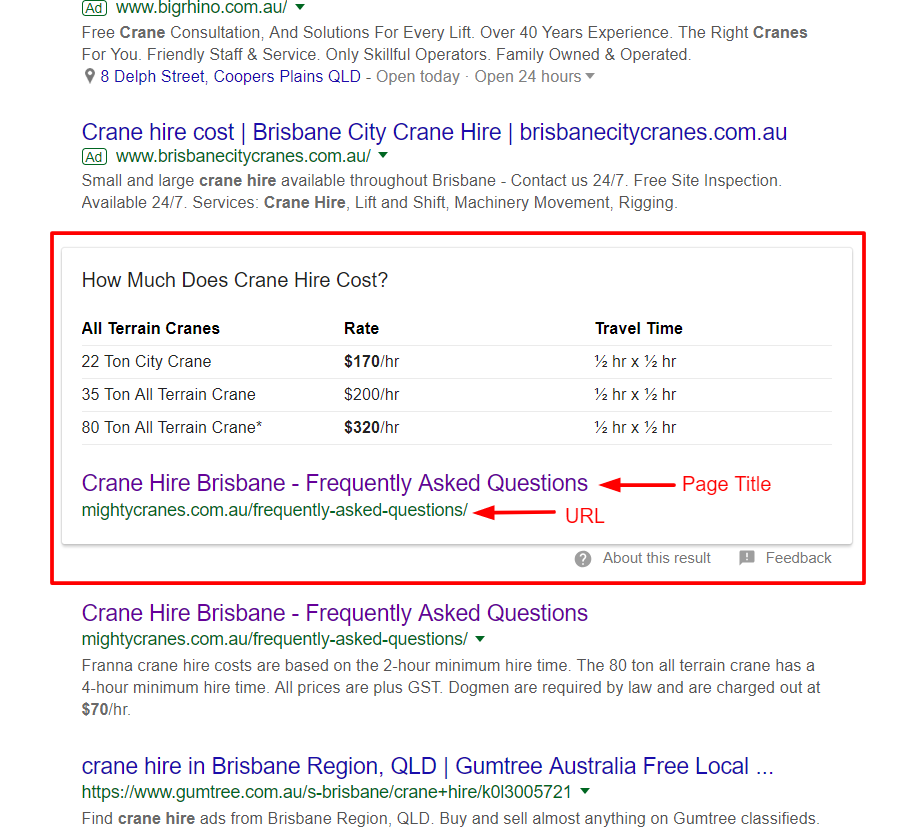
Featured Snippet
A featured snippet refers to a snippet of content in the form of a paragraph, list, or table, that is displayed directly below the paid ads, and above standard organic results. The content of a featured snippet is taken from a website that succinctly answers the search query. Featured snippets may also include an image taken from the same site as the snippet text.
Included in a featured snippet is the page title of the source page and the URL.
See an example of a table featured snippet below.
Google Penalty
A Google penalty is a punishment imposed by Google for breaking their user guidelines. This will result in a negative impact on the penalised website’s rankings.
There are two types of Google penalties; and automatic penalty and a manual penalty. An automatic penalty when Google crawls your site after an algorithm update and identifies that the quality guidelines have been broken (for example, if paid links are discovered).
Conversely, a manual penalty occurs when a Google team member identifies a website to be spammy or to be breaking the quality guidelines.
Both types of penalties will result in a drastic drop in your website’s rankings. However, unlike an automatic penalty, if you receive a manual action you will be notified in Google search console.
Header Tag
A header tag refers to a section of HTML code that represents the headings and subheadings on a page. Although people often refer to the h1 tag as the header tag, header tags actually range from h1 to h6 with h1 representing the most important heading, and h6 representing the least important heading.
For example, on this page the h1 tag (main title) is “Understanding SEO Terminology”. As with this article, the h1 tag is also generally the largest, boldest title. The subheading of this page (“Alt Text”, “Anchor Text”, “Backlink”, etc) are h2 tags as they are the second most important headings. If there were to be any headings beneath the subheadings, they would be h3 tags and so on and so forth.
See coded snippet below. The bold sections are the sets of header tags.
<h1>Main Heading<h1>
<h2>Subheading</h2>
<h3>Sub-Sub Heading</h3>
Internal Link
An internal link is a link from one page to another within the same domain. For example, if there is a link from the home page of your website to the product page of your website, that is an internal link. Conversely, if your home page links to the product page of another website, that is an external link.
Internal links can be used to make site navigation easier (eg. through a navigation menu), to help search engines crawl the website and to spread page authority throughout the site.
Keywords
In search marketing, keywords refer to the terms or phrases that you want your website to show up for. For example, if you own a nail salon in Brisbane, you would want your website to show up when users search “nail salon Brisbane”, so that would be one of your keywords.
Link Building
Link building is that act of obtaining new links from other domains to your website (see backlinks). This is a common practise in SEO as backlinks are one of the ranking signals used by Google and other search engines to determine the ranking of a website.
Local Search
A local search is a search performed on a search engine that is location specific. For example, the search query “nail salon Brisbane” is a local search, whereas, “nail salon” is not.
Local Search Marketing
Local search marketing is the process of ensuring that a local business ranks for local search queries (see local search). Local search marketing is used for local businesses and usually provides a high return on investment as 72% of consumers who perform a local search visit a store within 8kms.
Long Tail Keyword
A long tail keyword (see keyword) is a term or phrase that contains more words than a standard keyword (generally >3 words). The added length of a long tail keyword makes them more specific than standard keywords. Additionally, because long tail keywords are more specific, they will generally have a lower search volume than comparative standard keywords, making them less competitive to rank for.
Long tail keywords are often used to target potential customers early in the purchasing process. For example, if someone searches for “the benefits of a manicure” (a long tail keyword), they likely have not yet decided to get a manicure (early stages of the purchasing process).
Conversely, someone searching for “nail salon Brisbane” (a standard keyword) has likely already decided to make a purchase and is looking for somewhere to do so (later stages of the purchasing process).
Meta Descriptions
A meta description is a section of HTML code that represents a short page description. The meta description is the section of text that appears on the search engine results page (SERP) below the page title and URL (see image below).

Meta descriptions can be any length, however, the optimal length for a meta description is between 150 – 160 characters. This is because Google will usually cut off additional characters on the SERP.
Note: Google will sometimes extract a different snippet of content from the page to use as the meta description if it is more relevant to the searcher’s query.
Organic Traffic
Organic traffic is any traffic to your website that is generated via a search engine, such as Google or Bing, excluding paid traffic (see paid traffic).
Panda
Panda, in terms of SEO, refers to a major update to Google’s algorithm in 2011 that was focused on content quality. This algorithm update resulted in the decline in ranking of websites with thin content or low-quality content. Conversely, websites with quality content benefited from an increase in rankings.
Paid Traffic
Paid traffic is any traffic to your website that is generated via paid ads (eg. Google Ads).
Penguin
Penguin, in terms of SEO, refers to a major update to Google’s algorithm in 2012 that was focused on link quality. This algorithm update resulted in the decline in ranking of websites that had obtained links by violating Google’s quality guidelines (eg. through link farms or paid links).
PPC
PPC stands for pay per click, and refers to search marketing where a fee is charged for each click on a paid ad. One of the most popular platforms for PPC marketing is Google Ads.
SEM
SEM stands for search engine marketing. The term “search engine marketing” was originally coined to encompass both SEO (see SEO) and PPC (see PPC) marketing. However, search engine marketing is now generally only used to refer to PPC marketing.
SEO
SEO stands for search engine optimisation. SEO is the process of improving the ranking of a website on search engines. SEO is used to increase organic traffic (see organic traffic) to a website, as well as improve the quality of traffic received by a website. This ultimately results in more leads and sales.
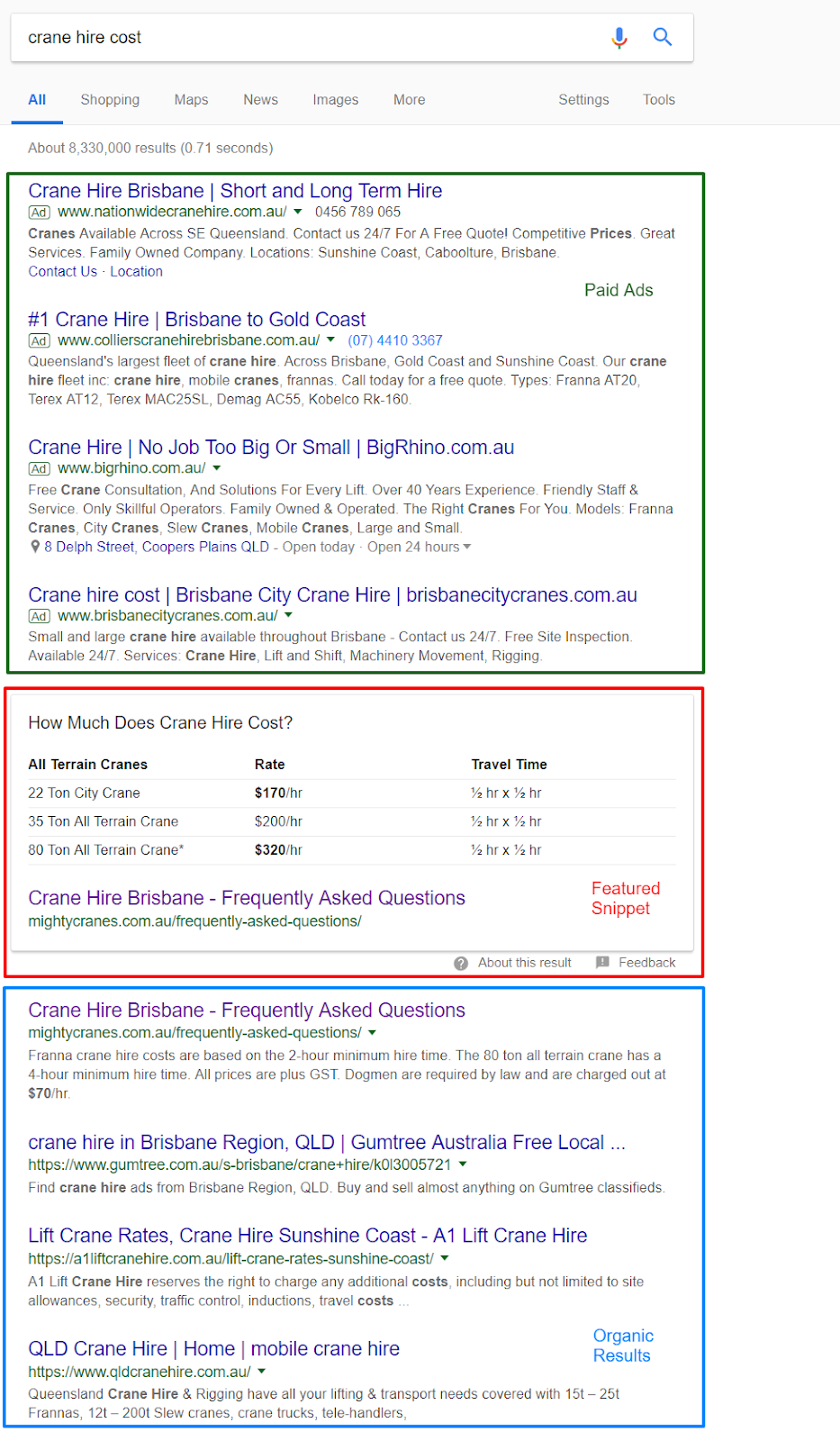
SERP
SERP stands for search engine results page. This is the page that is returned when a search query is performed on a search engine. The SERPs on Google include paid ads, featured snippets (see featured snippet) and organic results. (see below)
Title Tag
A title tag refers to section of HTML code that represents the page title. The page title is displayed in the SERPs and is also displayed in the tab at the top of the window (see below).
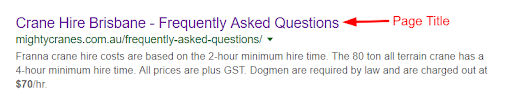

The title tag can be used to tell both users and search engines what the page is about.
White Hat SEO
White hat SEO is the opposite of black hat SEO (see black hat SEO). White hat SEO refers to SEO practises that are compliant with search engine guidelines. White hat SEO techniques are used to adjust a website to improve user experience and search engine rankings while staying within the search engine’s user guidelines.
White hat SEO is designed to provide lasting results in terms of increased traffic and rankings, without resulting in a Google penalty (see Google Penalty).
301 Redirect
A 301 redirect is when one webpage is permanently redirected to a different page. This means that when you click on a link to a permanently redirected page, or search for its URL, you will automatically be redirected to another page.
For example, if page A has a 301 redirect to page B, if you type the URL for page A into a
search bar, you will automatically be redirected to page B.
404 Error
A 404 error, or “404 not found” page, appears when a page can’t be found. This can occur when searching for a URL that has been changed or moved without redirecting the original URLor when a URL is misspelled.
For example, if your website’s product page used to be “example.com/product-range”, and the page URL has since been changed to “example.com/products”, people searching for the original page would instead be taken to a 404 error page. This can be avoided by placing a 301 redirect (see 301 redirect) on the original URL to the new URL.

